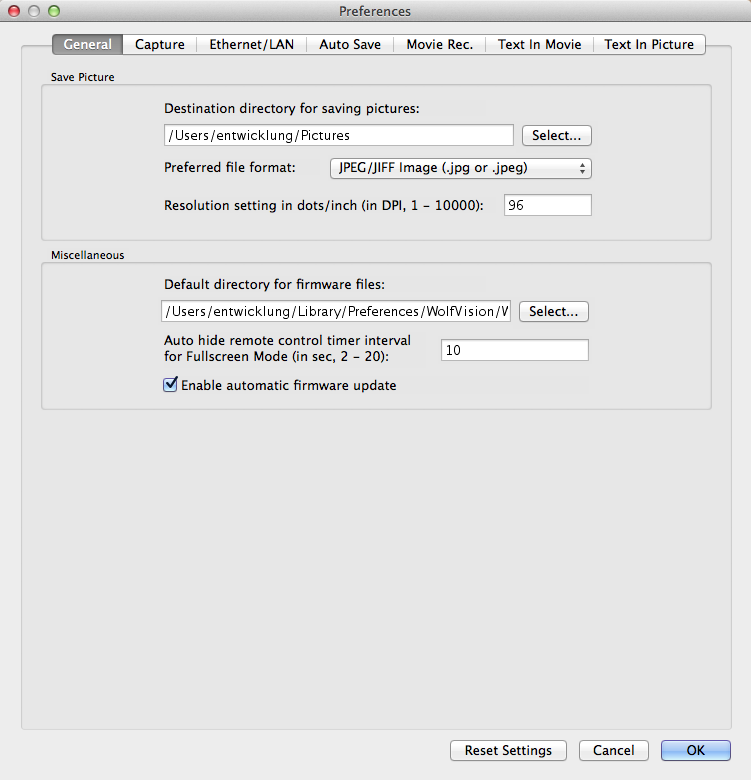
On this tab you can define the default directories for saving pictures and firmware files. It's also possible to define the amount of time the "Full Screen" mode remote control is displayed until it gets automatically hidden and if the application should perform an automatic check if there are updated firmware files available on the WolfVision web server.

To recall the default settings for this dialog tab, click "Reset settings". The other tabs of the "Preferences" dialog box will not be affected.
Click the "Select" button to change the destination directory for saving pictures with the "Save Picture..." menu item.
Select the pre-defined picture format for a saved picture. While saving a picture you can still change the used picture format. When JPEG format is selected, you also have to enter the JPEG quality value while saving a picture.
Picture formats can be divided into three categories: Lossy compression formats, lossless compression formats and uncompressed formats.
Uncompressed formats take up the most amount of data but they are exact representations of the picture.
Lossy compression formats are generally suited for photographs but not for illustrations, drawings and text as compression artifacts from the picture will be visible. Lossy compression, as its name implies, does not encode all the information of the picture so when it is decompressed for display it will not be an exact representation of the original. Lossy compression algorithms take advantage of the inherent limitations of the human eye and discard invisible information. Most lossy compression algorithms allow for variable quality level (compression) and as this level is increased, file size is reduced. At the highest compression level, picture deterioration becomes noticeable as "compression artifacting". However it is able to compress picture files very effectively compared to lossless formats, as it discards certain information. A prime example of a lossy compression format is JPEG (Pictures that have lots of complexity in them with similar colors throughout are good for this format).
Lossless compression formats are suited for illustrations, drawings, text and other material that would not look good when compressed with lossy compression. As the name implies, lossless compression will encode all the information from the original, so when the picture is decompressed, it will be an exact representation of the original. Because there is no loss of information in lossless compression, the achievable compression level is normally lower than with lossy compression. Examples of lossless picture compression are PNG and GIF. GIF supports only 256 colors (8 bits per pixel). PNG supports a wider range of formats from 8 bits per pixel to 24 bits per pixel. PNG is the mostly used today due to its flexibility and compression.
The use of a certain picture compression depends on what should be compressed. Possible file formats are:
Microsoft Bitmap Graphic (.bmp) The BMP file format (Windows bitmap) handles graphics files within the Microsoft Windows OS. Typically, BMP files are uncompressed, hence they are large; the advantage is their simplicity, wide acceptance and use in Windows programs.
JPEG/JIFF Image (.jpg or .jpeg) JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) files are (in most cases) a lossy format; the filename extension is JPG or JPEG. Nearly every digital camera can save pictures in the JPEG format, which supports 8 bits per color (red, green, blue) for a 24-bit total, producing relatively small files. If the compression level is not set too high, it does not noticeably detract from the picture's quality, but JPEG files suffer generational degradation when repeatedly edited and saved. Photographic pictures may be better stored in a lossless format if they will be re-edited, or if small "artifacts" (blemishes caused by the JPEG's compression algorithm) are unacceptable. The JPEG format also is used as the picture compression algorithm in many Adobe PDF files.
PC Paintbrush Bitmap Graphic (.pcx) PCX is a device-independent raster image format; the file header stores information about the display hardware (screen resolution, color depth and palette information, bit planes and so on) separately from the actual image information, allowing the image to be properly transferred and displayed on computer systems with different hardware. PCX files commonly store palette-indexed images ranging from 2 or 4 colors to 16 and 256 colors, although the format has been extended to record true-color (24-bit) images as well. It's a lossless bitmap image format.
Portable Network Graphic (.png) The PNG file format was created as the free, open-source successor to the GIF. The PNG file format supports truecolor (16 million colours) while GIF only supports 256 colors. The PNG file excels when the picture has large, uniformly colored areas. The lossless PNG format is best suited for editing pictures and the lossy formats, like JPG, are best for the final distribution of photographic pictures, because JPG files are smaller than PNG files. Many older browsers currently do not support the PNG file format, however, with Internet Explorer 7, all contemporary web browsers fully support the PNG format. The Adam7-interlacing allows an early preview, even when only a small percentage of the picture data has been transmitted.
PBM Portable AnyMap Graphic (.ppm) PPM (Portable Pixmap Format) is a lossless bitmap image format for true-color (24-bit) images. It is not compressed and thus requires more space and bandwidth than a compressed format would require. The PPM format is generally an intermediate format used for image work before converting to a more efficient format, for example the PNG (Portable Network Graphics) format, without any loss of information in the intermediate step.
Raw RGB 24-bit Graphic (.raw) Lossless bitmap format with no header which stores a true-color (24-bit) bitmap.
Silicon Graphics IRIS Graphic (.sgi)
Tagged Image Format (.tif) The TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is a flexible format that normally saves 8 bits or 16 bits per color (red, green, blue) for 24-bit and 48-bit totals, respectively, using either the TIFF or the TIF file extensions. The TIFF's flexibility is both a blessing and a curse, because no single reader reads every type of TIFF file. TIFF's are lossy and lossless; some offer relatively good lossless compression for bi-level (black&white) images. Some digital cameras can save in TIFF format, using the LZW compression algorithm for lossless storage. TIFF is not widely supported by web browsers. TIFF remains widely accepted as a photograph file standard in the printing business. TIFF can handle device-specific colour spaces, such as the CMYK defined by a particular set of printing press inks.
The following list is a brief summary for the available picture formats when using them within a web page/application.
BMP shouldn't be used online within web pages - wastes bandwidth
JPEG is great for photos
PNG is great for illustrations and photos. PNG is a fair replacement for GIF and JPG and has the best support for transparency.
This setting is used by picture editing applications to determine the resulting size of a picture on a piece of paper. Default value is 96 DPI.
Click the "Select" button to change the directory for the firmware file repository which is used for updating the firmware version of WolfVision devices.
This setting controls the amount of time the remote control will be visible while the application is running in "Full Screen" mode.
To allow the application to automatically check for newer firmware files available for firmware updates from the WolfVision web server, check this box. If you've activated the automatic firmware update you don't have to organize any firmware files for the update process because this is all done by the application itself. Nevertheless you are asked if you really want to download the latest firmware files from the WolfVision web server if there are newer versions available. In order to work correctly, a Internet connection is necessary to check for newer firmware file versions. The automatic search for firmware files in your local firmware file repository will still work even if no Internet connection is present.